Analytical Services Section
PCB Aroclor Analysis by GC-ECD & Congener/Homolog Analysis by LRMS
Traditionally, most PCB analysis has been performed by either of two approaches - aroclor analysis, that utilizes gas chromatography with an electron capture detector (GC-ECD); or congener/homolog analysis that employs high resolution gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/HRMS). While each approach has its advantages and disadvantages, there is a substantial gap between these techniques in terms of the type, depth, breadth, and quality of information and price. Alpha offers both aroclor and congener/homolog analysis. The following represents an overview of PCB aroclor analysis by GC-FID as well as a GC/LRMS approach for the analysis of PCB congeners and homologs.
PCB Aroclor Analysis
Historically, the vast majority of PCB analyses conducted in support of remedial investigations and feasibility studies were determinations of PCB aroclors utilizing gas chromatography-electron capture detector (GC-ECD). While this is still the case today, as the inadequacies of aroclor determination for human health and ecological risk assessment has become more apparent. This is particularly true for sediment and tissue analysis, as regulatory criteria and guidance has shifted towards PCB congener and homolog analysis.
However, PCB aroclor analysis still has its place, primarily due to its relatively low cost. This is especially true for sites that have been previously well characterized, where the site-specific limitations of the aroclor analyses are known and the sample matrix is not overly challenging. At a minimum, aroclor analysis can be used as a screening tool to direct subsequent congener and/or homolog analysis.
Alpha Analytical performs PCB aroclor analysis in accordance with EPA Method 8082, whereby. sediment samples are generally extracted utilizing EPA Method 3570 - Microscale Solvent Extraction (MSE). Sample extracts can then be 'cleaned up' to minimize interferences using silica gel, or gel permeation chromatography (GPC), as necessary.
PCB Congener & Homolog Analysis by LRMS
The primary disadvantages of aroclor analysis by GC-ECD are qualitative in nature, because chromatographic patterns and peak ratios are subject to change in the environment due to "weathering." PCB aroclors may be reported as not detected, due to a lack of pattern recognition, although PCB congeners may actually be present or quantified as a different aroclor. Quantitatively, it can also be difficult to determine a total PCB concentration using the aroclor approach. This is especially true when more than one aroclor is determined to be present. As the individual aroclors represent mixtures of PCB congeners, there is a possibility that "double counting" of PCBs could also occur.
PCB analysis utilizing GC/LRMS (gas chromatography/low resolution mass spectrometry) can be a solid alternative for some data collection applications. This method also represents an effective compromise between the aroclor option by Method 8082 and the HRMS congener analysis by Method 1668a. Alpha Analytical utilizes a GC/LRMS procedure for PCB congener and homolog analysis based on EPA Method 680 and EPA Method 8270, as well as the NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-NWFSC-59, March 2004.
This procedure can determine all 209 PCB congeners or a subset of congeners (WHO, NOAA or a custom list). The GC/LRMS method can be a very cost effective option for characterizing contaminated samples for PCB congeners. In addition, this method can also measure groupings of PCB congeners as a function of their level of chlorination (e.g. homologs). The homolog determination provides another, more representative option for the determination of "total PCBs". Homolog analysis can be included with the congener analysis or reported separately.
PFAS Analysis of Drinking Water by EPA Method 533
Alpha Analytical now offers PFAS analysis of drinking water by EPA METHOD 533: DETERMINATION OF PER- AND POLYFLUOROALKYL SUBSTANCES IN DRINKING WATER BY ISOTOPE DILUTION ANION EXCHANGE SOLID PHASE EXTRACTION AND LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY/TANDEM MASS SPECTROMETRY. This new PFAS analytical method was released by EPA in December 2019 and it includes some significant improvements over the existing EPA PFAS drinking water procedure, Method 537.1.
There are two primary procedural differences between the methods. Method 533 incorporates the use of extracted internal standards as part of an isotopic dilution quantification approach whereas Method 537.1 does not. The use of the isotope dilution technique reduces the overall uncertainty associated with the analysis. Method 533 also uses a weak anion exchange (WAX) solid phase extraction (SPE) cartridge instead of the polystyrene divinylbenzene (SDVB) used in Method 537.1. The use of the WAX SPE cartridge in Method 533 allows for additional PFAS compounds to be determined, particularly short chain PFAS not amenable to Method 537.1 analysis.
Method 533 lists 25 PFAS compounds that can be analyzed by the method and Method 537.1 lists 18 PFAS compounds. It should be noted that not all 18 of the Method 537.1 compounds can be determined by Method 533, even though it has a 25 compound list. The Method 533 list contains 14 Method 537.1 compounds, plus 7 additional compounds that are on DoD and other compound lists, as well as 4 totally new PFAS compounds that were previously not on any PFAS analytical list. Therefore, the maximum number of PFAS compounds that drinking water can be analyzed for using EPA compliance methods is 29 by using both Methods 537.1 and 533 to analyze the sample.
Another significant difference between the two methods are the holding times required by each. Method 533 allows for 28 days to extraction and 28 days to analyze whereas Method 537.1 only allows 14 days to extraction and 28 days to analyze. There are different preservatives used as well, ammonium acetate is used for Method 533 and Trisma is used with Method 537.1.
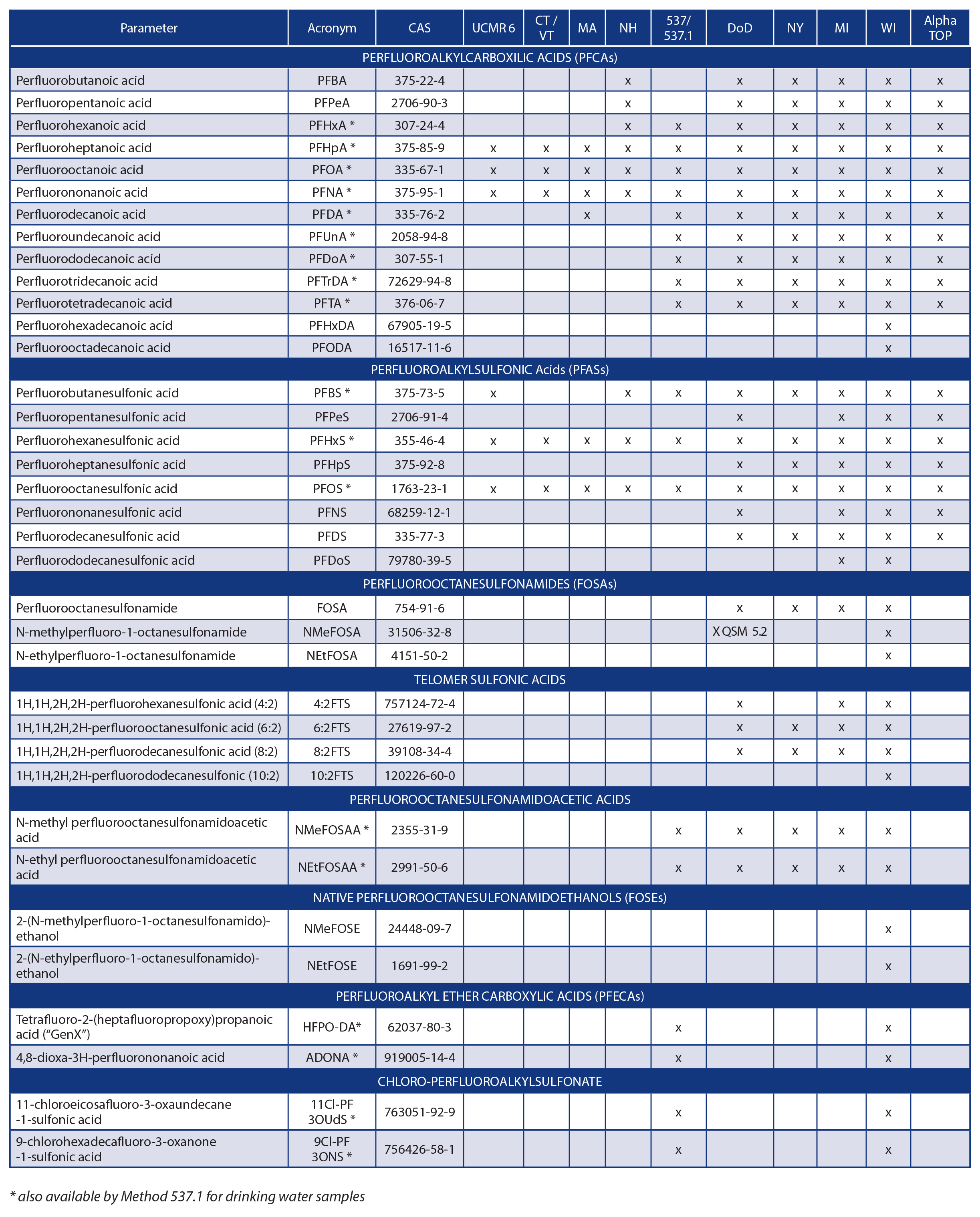
Please see the table below that lists the two EPA drinking water target compounds as well as the Alpha proprietary isotope dilution and Total Oxidizable Precursors (TOP) PFAS target compound lists.
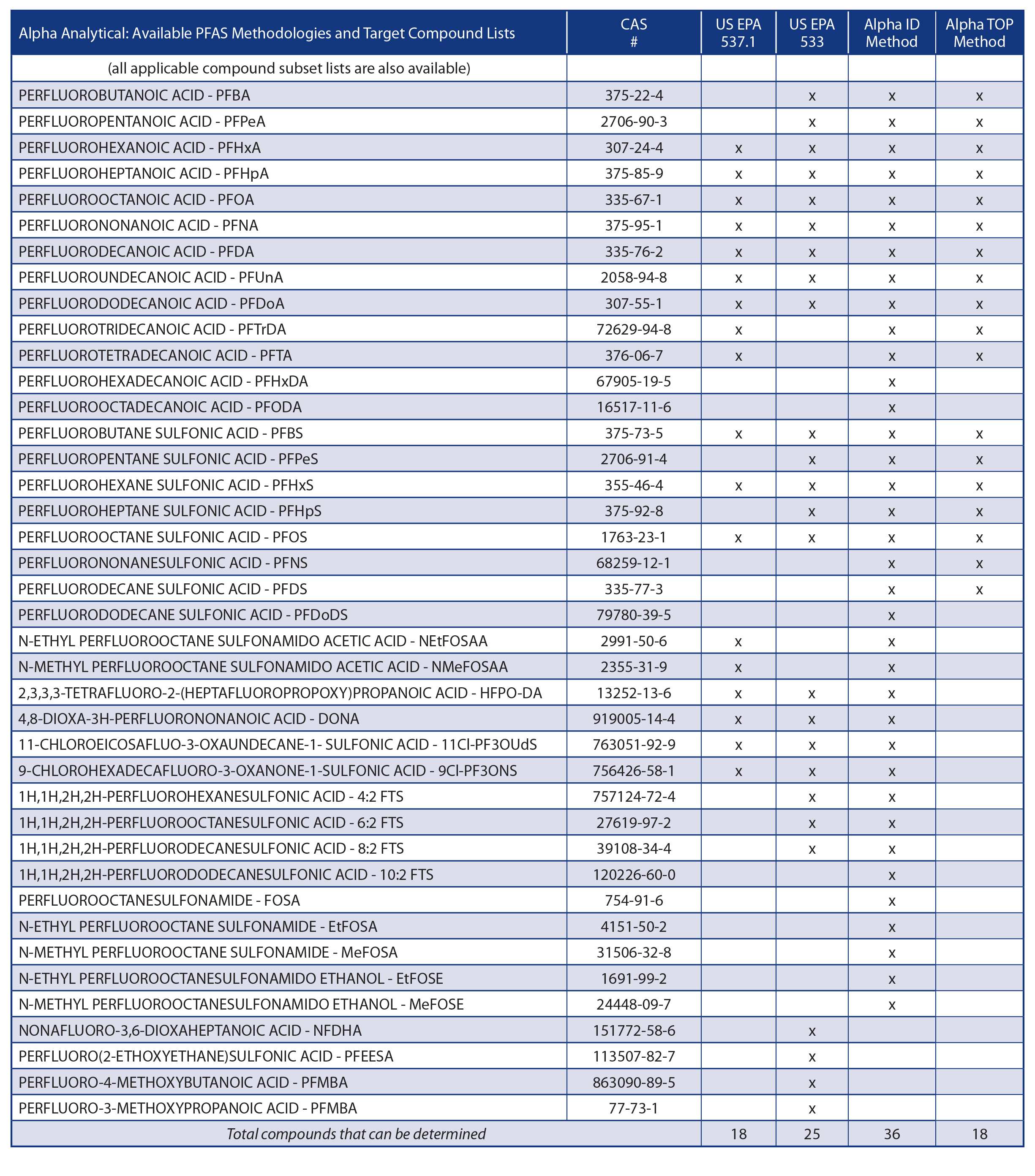
Per and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Compound List
Alpha Analytical's List of 36 Compounds
Contact Alpha Analytical today for all your Emerging Contaminant needs or if you have any questions.
Call 800-624-9220 or email us at .
Low Volume Initiative (LVI)
 Alpha Analytical recognizes the challenges of conducting routine water sampling in a highly competitive market. Alpha now offers a Low Volume approach to specific extractable analysis. We undertook this initiative in effort to advance it’s technology offerings, reduce sample collection efforts, minimize the use of organic solvents and reduce waste. This technique employs the same methods as before using less sample volume and less analytical reagents.
Alpha Analytical recognizes the challenges of conducting routine water sampling in a highly competitive market. Alpha now offers a Low Volume approach to specific extractable analysis. We undertook this initiative in effort to advance it’s technology offerings, reduce sample collection efforts, minimize the use of organic solvents and reduce waste. This technique employs the same methods as before using less sample volume and less analytical reagents.
Please see the attached Technical Bulletin or contact your sales representative for more information.
Vapor Intrusion State Table
What do I need to know about Vapor Intrusion Testing in neighboring state?
The matrix is provided to assist in giving a basic understanding for laboratory requirements for air testing to support Vapor Intrusion (VI) programs in New England and Mid-Atlantic States.
State VI guidance are accessible by web search. However, some are much more user friendly than others. Alpha Analytical maintains NELAP accreditation in states who offer certification.
Connecticut and Massachusetts have self-certification programs which requires the laboratory to complete a QA/QC evaluation which is included in the laboratory deliverable. The state reviews laboratory data deliverables in the process of reviewing site reports submissions.
A number of states do not offer state Certification/Accreditation for air methods. Alpha Analytical is your partner for Air and Vapor Intrusion testing in which ever state your project is located.
| New England States | ME | NH | MA | VT | CT | RI |
| State Regulatory Agency | MEDEP | NHDES | MassDEP | VTDEC | CTDEEP | RIDEM |
|
State Program/Guidance |
RPG | SRP | MCP | IROCP | RSR | IRHMR |
| NELAP Accreditation* | Y | Y | N | N | N | N |
| State Certification (Air) | Y | Y | CAM | Y | RCP | N |
| State Deliverables | N | N | Y | N | Y | N |
| Stand-alone VI Guidance / Fact Sheet | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N |
| Specific VI Compound List | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N |
| TO-15 SIM Required for VISL | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Screening Tables | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N |
| Comments | ||||||
| Laboratory Clearly Defined | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | N |
| User Defined | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y |
| Mid-Atlantic States | NY | NJ | PA | DE | MD | DC |
| State Regulatory Agency | NYSDEC/ NYSDOH | NJDEP | PADEP | DNREC | MDE | DCDOEE |
|
State Program/Guidance |
DER | SRP | ACT 2/TGM | SIRB | LRP/VCP | DCRBCA |
| NELAP Accreditation* | Y | Y | N | N | N | N |
| State Certification (Air) | ELAP | Y | N | N | N | N |
| State Deliverables | Y | Y | N | N | N | N |
| Stand alone VI Guidance / Fact Sheet | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Specific VI Compound List | Y/N | Y | N | N | N | N |
| TO-15 SIM Required for VISL | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Screening Tables | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Comments | ||||||
| Laboratory Clearly Defined | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y |
| User Defined | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y |
* States without Air certification prefer data reported by a laboratory with NELAP Accreditation for methods reported.
Recent state guidance updates include: the New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection (NJDEP) technical guidance document notice dated 01-18-18 (revision 4.1) and corresponding change log can be found on the SRP Guidance Library (www.nj.gov/dep/srp/guidance/)
Contact Alpha Analytical today for all your Vapor Intrusion and Air Testing needs.
To speak to one of our technical experts please fill out the form to your left.
Subcategories
Analytical Services Category Article Count: 12
Analytical Services Content Feature Article Count: 3
What Our Clients Are Saying
- “Every job is treated like the most important one that Alpha is doing. I…»»